When comparing Lean Six Sigma vs Six Sigma as training or certification programs, the difference is simple and easy to understand: Lean Six Sigma combines Lean management and Six Sigma into a single program, whereas Six Sigma focuses exclusively on the Six Sigma methodology.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
What is Six Sigma?

Six Sigma is a data-based method that tries to reduce variation in a process. It was created by Motorola in the 1980s and later became well-known through companies like General Electric. Its goal is to reach almost perfect quality — about 3.4 defects in one million chances.
The approach follows a structured problem-solving model known as DMAIC:
- Define: Identify the problem and customer requirements.
- Measure: Collect data and establish current performance levels.
- Analyze: Determine the root causes of defects.
- Improve: Implement solutions to address those causes.
- Control: Monitor results to sustain improvements.
Six Sigma uses numbers and data tools to make decisions. It works best for companies that need careful and consistent production or service.
Learn about the roles and responsibilities of Six Sigma professionals in our guide: Six Sigma roles Explained.
What is Lean manufacturing?
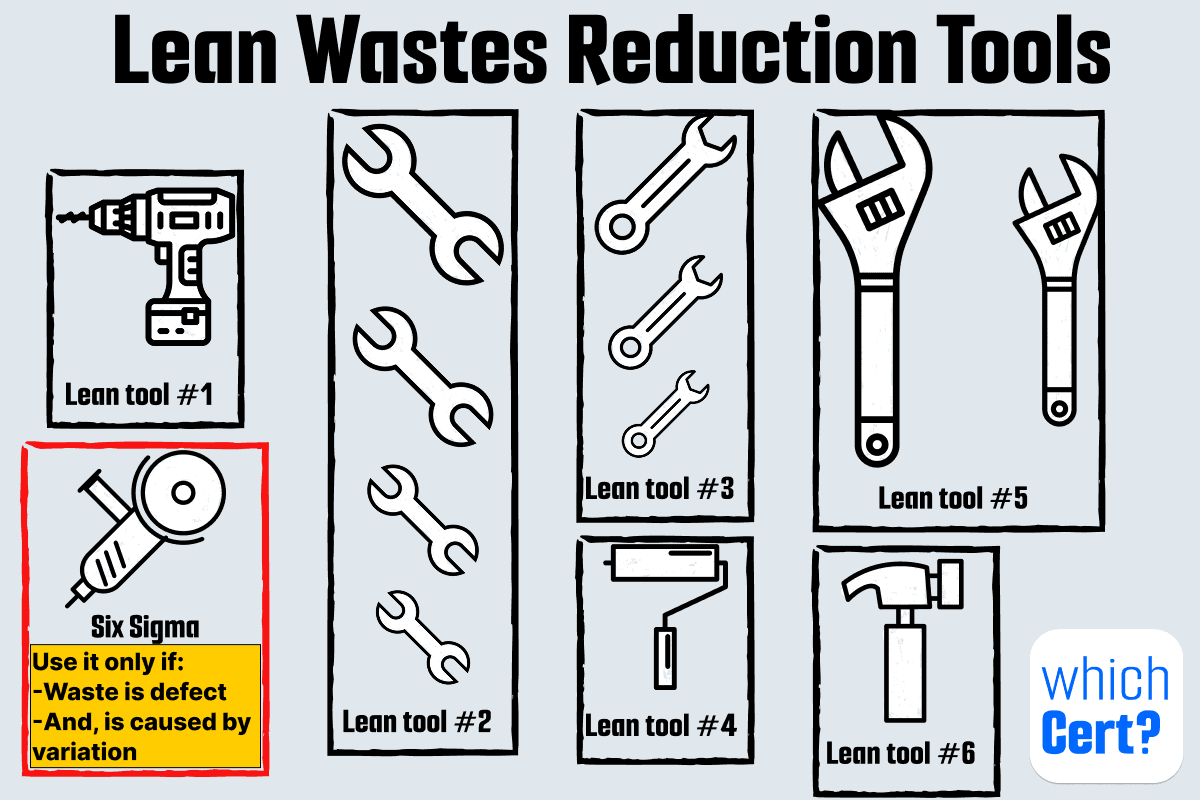
It is an improved way to run manufacturing. It focuses on cutting waste (see the seven wastes) and controlling costs by using the following methods and tools (non-exhaustive list):
- Visual management
- 5S: Sort, set in order, shine, standardize, sustain
- TPM: Total productive maintenance
- Value stream mapping
- Quick set ups and short cycle times
- Heijunka: Leveled production plan
- SPC methods for control
- Poka-yoke: Error prevention
- Jidoka: 100% inspection and stopping defectives
The aim of all those tools is to deliver to customer a product:
- Of high quality
- In the right quantity
- At least price
Lean Manufacturing (Toyota Production System) helped Toyota grow from a small local car maker in the mid-1900s into one of the most competitive car companies in the world.
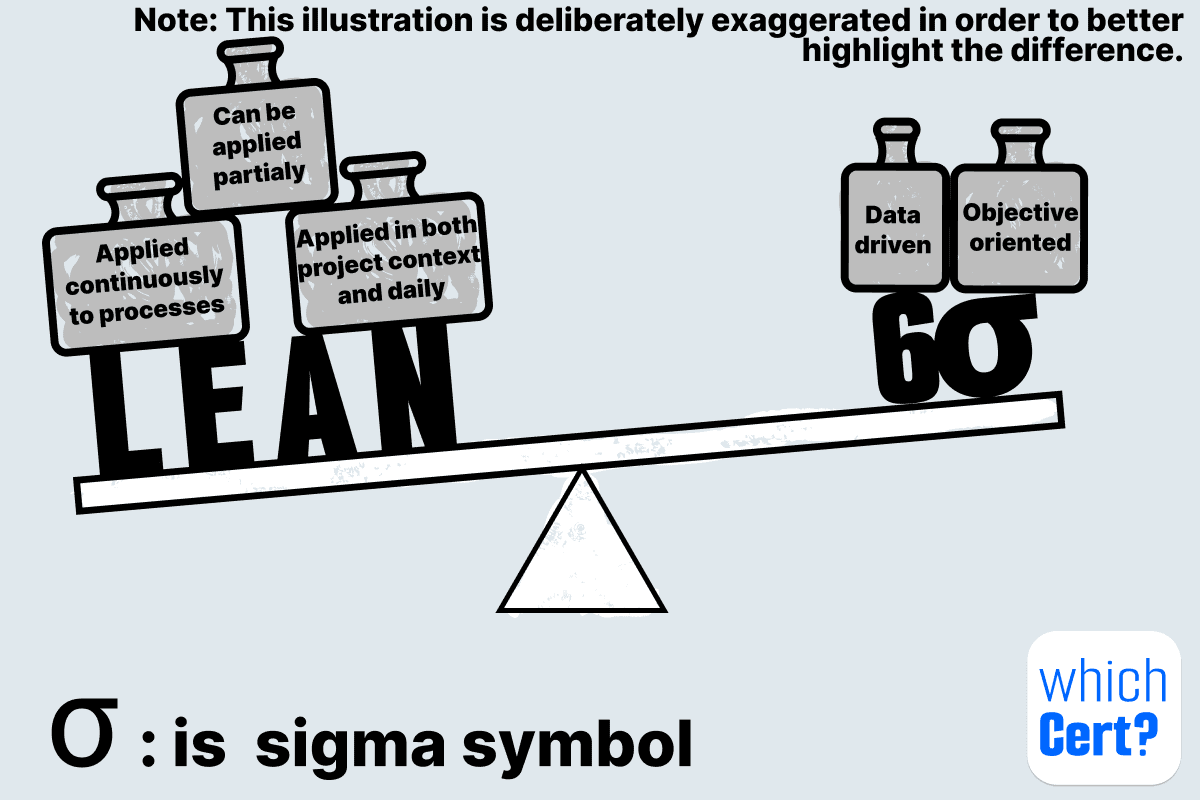
Lean Manufacturing vs Six Sigma: what’s the difference?
| Aspect | Lean | Six Sigma |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduce waste and improve flow. | Reduce process variation and defects. |
| Application Scope | Can be applied partially; companies may use selected tools (5S, JIT, Kaizen, etc.). | Must follow the complete DMAIC methodology end-to-end. |
| Process Coverage | Applies across all company processes (operations, logistics, administration, customer service, etc.). | It can be used for any process with measurable results, like production or services such as finance, healthcare, or support. |
| Execution Mode | Continuous improvements or project-based. | Always project-based with a defined start and end. |
| Complexity | Some tools are relatively easy to implement (5S, visual management, waste elimination). | Strongly data-driven; requires statistical analysis and measurement systems. |
| Goal Definition | It often tries to reach several goals at once, like cutting production time and making just-in-time delivery possible. | It always begins with one clear, measurable problem. For example, a 0.1% defect rate, which is too high in high-quality settings. 0.1% = 1,000 defects per million → far from Six Sigma level |
| Problem Examples | “Reduce lead time, reduce inventory, and improve flow simultaneously.” | “Current defect rate is 0.1% — we need to identify root causes and reduce it toward Six Sigma levels.” |
Is 6 sigma part of Lean?
Lean counts defects as one of its seven wastes, so reducing defects is already part of Lean. However, Six Sigma helps even more by cutting defects caused by process variation.
What does TIMWOOD mean? (7 wastes)
It is an acronym for the seven wastes in Lean manufacturing, called the “mudas”. Later, “Skills” was added, and the acronym became TIMWOODS:
- Transportation of raw material or product moved unnecessarily over long distances.
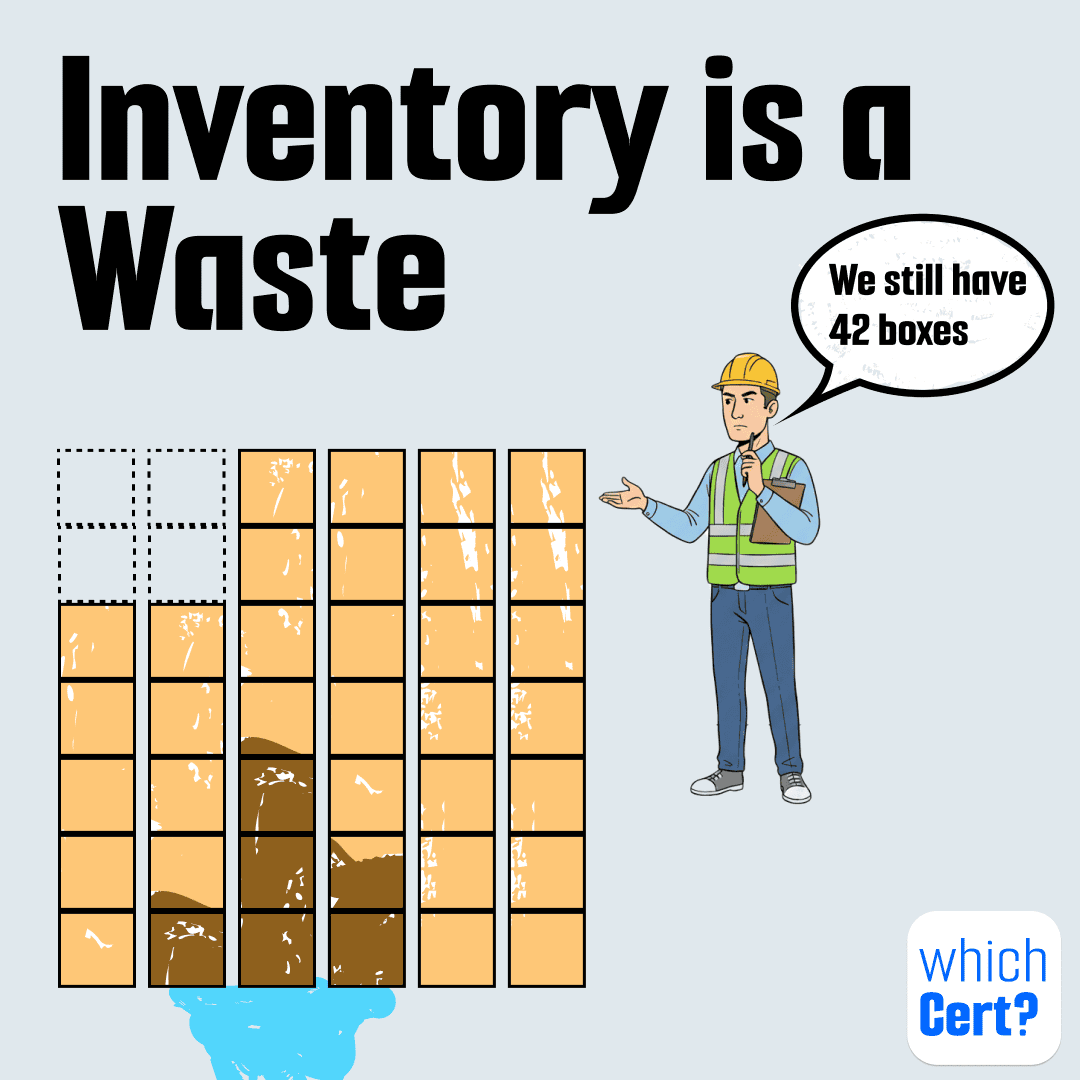
- Inventory: products or in-process material siting in inventory.
- Motion: unnecessary movement of people or equipment. A good example is a Formula 1 pit crew.
- Waiting time of workers.
- Overproduced units: making a product before it is actually needed. For example, a cold hamburger made minutes before you order it.
- Over-processing: unnecessary operations performed.
- Defective units produced.
- Skills: unused talents.
For example: Inventory is not an asset. In Lean, it’s waste.
Excess inventory doesn’t just take space. It hides problems:
- Defects stay invisible when products sit in storage
- Quality issues get discovered too late
- Obsolete or damaged items pile up quietly
And beyond operations, there’s a financial cost. Inventory freezes cash that could be invested in growth, innovation, or customers.
Lean isn’t about having zero inventory. It’s about having only what creates value, when it creates value.
What is the meaning of DMADV?
DMADV is the less famous Six Sigma project structure. It stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify, and it’s used when creating a new process.
Lean Six Sigma certification vs Lean Six Sigma
When browsing the internet, don’t get confused. Lean Six Sigma is a method used in companies, but Lean Six Sigma certification is a professional certificate for people, not a company certificate like ISO 9001.
Should I do Lean or Six Sigma first?
Six Sigma uses data that reacts to small changes. But it doesn’t make sense to focus on tiny process tweaks when basic problems, like a messy workplace that 5S can fix, are still there and can cause big issues. In short, don’t chase small changes before fixing the bigger, obvious problems.
It also depends on what the customer wants. In industries where exact specs matter, like cars, Six Sigma is often a must for clients. On-time delivery, which Lean focuses on, can be discussed, but meeting exact specs cannot.
On the other hand, a delivery company may prioritize removing waste to speed up delivery times, which makes Lean the better fit.
Final thoughts
So, Lean Six Sigma vs Six Sigma: which is better?
It really comes down to what you want.
Lean Six Sigma gives you the widest career options because you learn both Lean and Six Sigma in one program. If you want something quicker, a Six Sigma-only certification is faster. And in the U.S. public sector, Lean Six Sigma is even the recommended choice.
Read our 5-step guide to learn how to earn a recognized Six Sigma certification.
FAQ
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a method that combines Lean, which cuts waste and improves flow, with Six Sigma, which improves quality and reduces defects.
Which Six Sigma certification is most recognized?
Six Sigma accreditation isn’t governed by a single global authority. In fact, programs offered by reputable institutions and universities—though not formally accredited—are often equally respected. The best-way to choose the right certification is to consider your experience level and your career objective.
Check this guide to fully answer to: Which Six Sigma certification is most recognized?
What are the two types of Six Sigma?
The most common project framework is DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control). There is also DMADV, a less famous framework that stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify, used specifically for designing new processes.
What is the main goal of a Six Sigma implementation?
The main goal of Six Sigma implementation is to reduce variation in a process.

